What is the construction of a transformer and the function of each component? Anyone know in such detail?
1. What should I do when the secondary circuit is not open (open)?
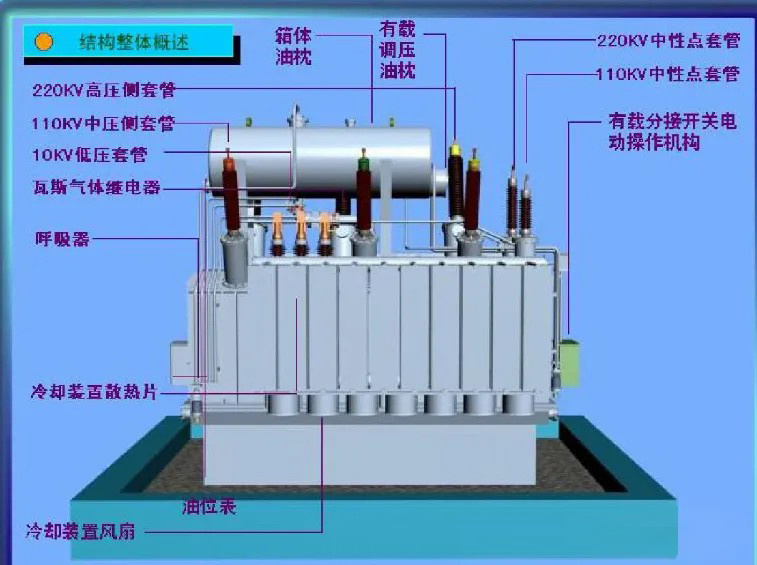
The transformer is mainly composed of iron core, coil, insulating material, oil tank, oil conservator, insulating sleeve, tap-changer and gas relay, radiator, etc
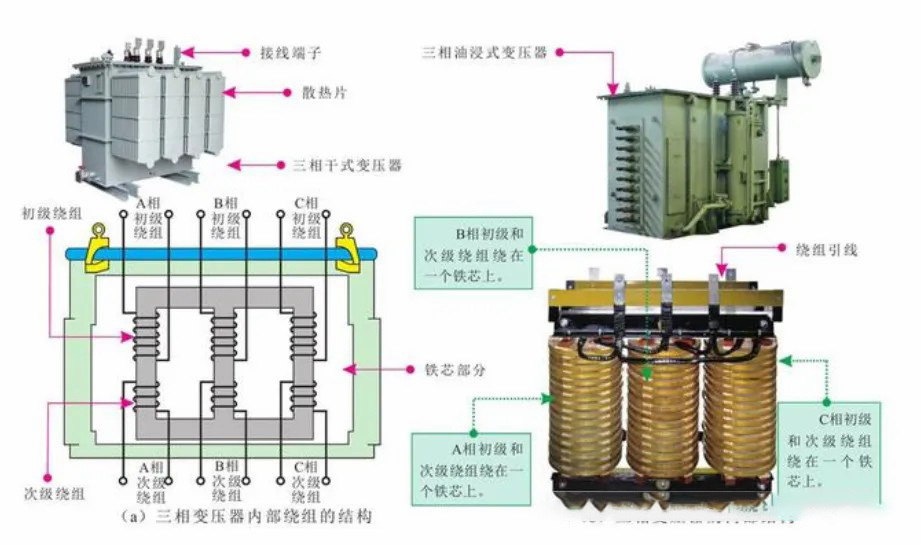
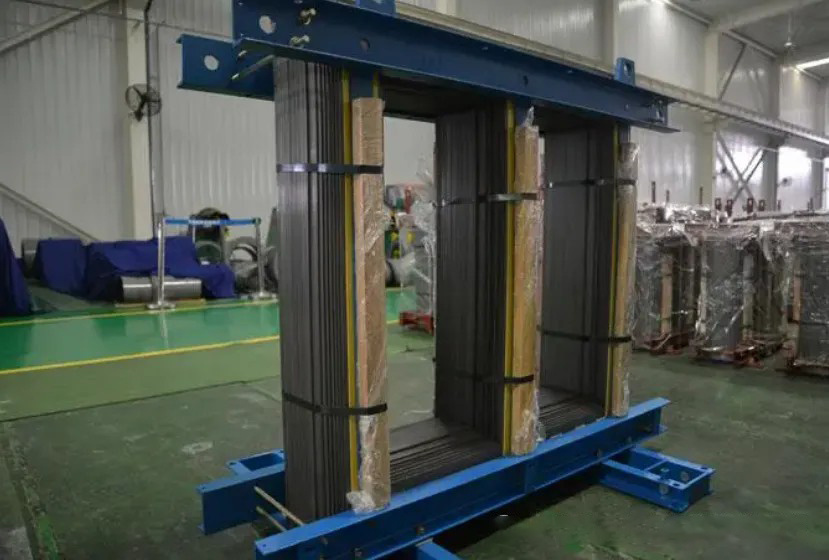
1. The core
is made of superimposed silicon steel sheets: the thickness of the silicon steel sheets is usually 0.35 mm or thinner, and these sheets are coated with insulating paint to reduce eddy current losses. The iron core provides a magnetic circuit with low resistance to the magnetic flux, which enhances the magnetic flux coupling and reduces magnetic loss. Provide mechanical support for transformer windings.

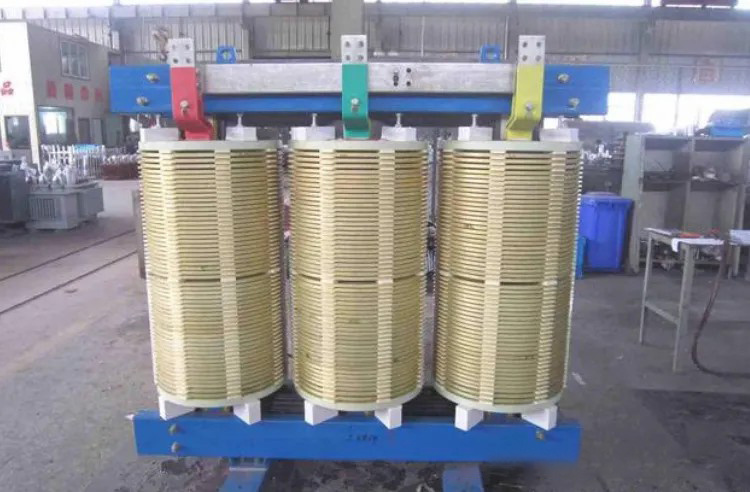
2.
Winding primary winding and secondary winding: Depending on the purpose of the transformer, the number of turns of the primary and secondary windings is different to achieve different voltage conversions. The windings are usually made of insulated copper or aluminum wires. The electrical energy of the primary winding is transmitted to the secondary winding through electromagnetic induction to realize the conversion of voltage and current. Electrical isolation between the high-voltage and low-voltage windings ensures safety.

3. Insulating materials: insulating paper
, insulating varnish, etc.: used for insulation between windings and between windings and iron cores. Electrical isolation: Prevent short circuits between windings and ensure the normal operation of the transformer. Thermal heat dissipation: Helps dissipate heat and prevents overheating from damaging the transformer.
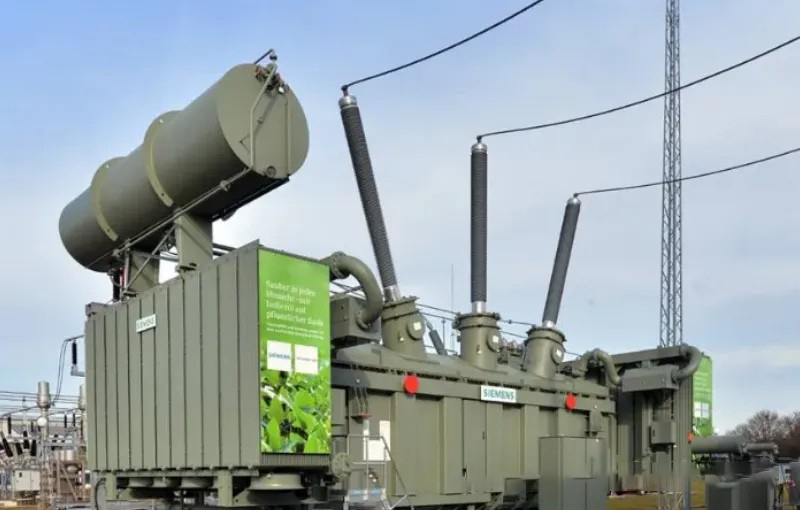
4. Oil tank (oil-immersed transformer)
Steel oil tank: Contains transformer oil, usually mineral oil. The transformer oil dissipates heat by convection, taking away the heat generated during the operation of the transformer. On the other hand, oil is used as an insulating medium to improve insulation performance and prevent electrical breakdown.

5. The oil pillow (expander)
is installed on the top of the fuel tank and is usually connected to the fuel tank through a pipe. When the volume of transformer oil expands or decreases with the temperature of the oil, the oil conservator plays the role of oil storage and oil replenishment, so as to ensure that the oil tank is full of oil. At the same time, due to the installation of an oil storage cabinet, the contact surface between the transformer and the air is reduced, and the deterioration rate of the oil is reduced. The side of the oil conservator is also equipped with an oil level gauge (oil mark pipe), from which the oil level can be monitored for changes in the oil level.
In the oil storage cabinet of some transformers, there is an oil-resistant nylon rubber bag. The outside is oil, the inside is air, and the film is used to isolate the oil from the air and slow down the deterioration of the oil.
There is also a small pipe communication between the oil conservator and the explosion-proof pipe, so that the air pressure and oil level in the two places are the same, and the malfunction of the gas relay caused by the change of oil level is avoided.
6. Radiator (cooling system)
Sheet radiator or tubular radiator: installed outside the oil tank, through natural cooling or forced air cooling, forced oil cooling. Cools the transformer oil faster and keeps the transformer operating within a safe temperature range.
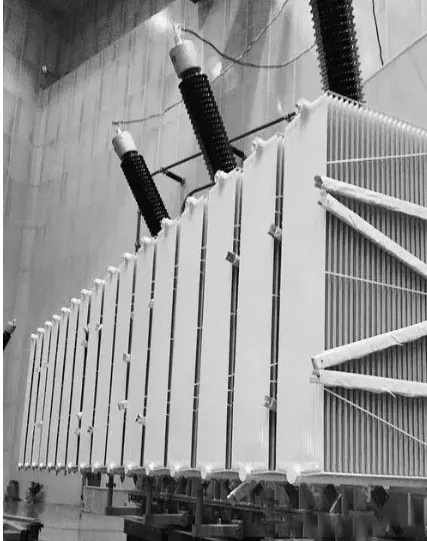

7. Protective device
explosion-proof pipe: installed on the upper part of the fuel tank. The flared tube communicates with the oil conservator or atmosphere, and the nozzle is sealed by a membrane. When there is a fault inside the transformer, the oil temperature rises, and the oil is violently decomposed to produce a large amount of gas, which increases the pressure in the oil tank, and then the explosion-proof pipe film is broken, and the oil and gas are sprayed out from the nozzle to prevent the explosion or deformation of the oil tank of the transformer.
Thermostat: Monitors the temperature of the transformer to prevent overheating.
The pressure relief valve releases pressure when the internal oil pressure is too high, preventing the fuel tank from exploding.
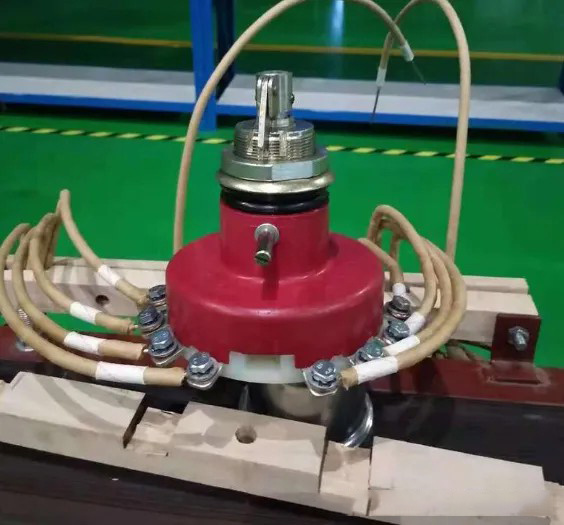
8. Leads & Bushing
High Voltage Bushings and Low Voltage Bushings: Made of insulating materials, they are used to connect the wires leading out of the internal windings of the transformer to external circuits.
Electrical Connection: Electrically connect the inner windings of the transformer to an external circuit.
Insulation Protection: Ensure that the leads are electrically insulated as they pass through the transformer housing.
9.
On-load voltage regulation switch (OLTC) or non-load voltage regulation switch (NLTC): adjust the output voltage of the transformer according to the load situation and grid voltage situation. It is a device for adjusting the transformer ratio. The primary coil of the double-turn transformer and the primary and secondary coils of the three-turn transformer generally have three to five split positions (the middle split 2 of the three taps is the position of the rated voltage, and the difference between the adjacent splits is 5%; The difference between the adjacent splits of the transformer with multiple splits is 2.5%), and the operating part is installed on the top of the transformer and extends into the oil tank of the transformer through the transmission rod. According to the needs of the system operation, according to the indicated marking, to select the position of the split, some transformers are equipped with on-load voltage regulating devices.

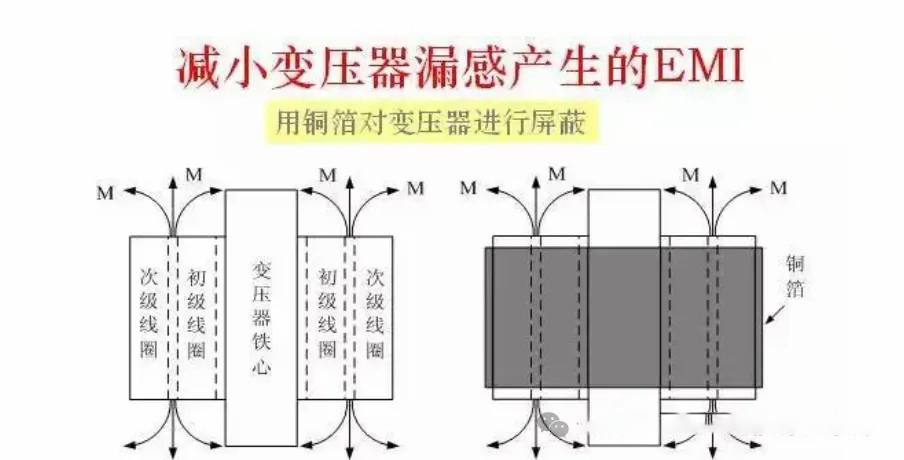
10. Conductive materials such as magnetically shielded and electrically shielded
copper or aluminum plates, installed between windings or iron cores. Reduce magnetic flux leakage loss and magnetic flux interference to surrounding equipment.
Electrical shielding: Reduce the interference of the electric field to the surrounding equipment and prevent the loss caused by the coupling of the electric field.
11. Gas relay: It is the main protection device of the transformer, which is installed on the connecting pipe of the oil tank and the oil conservator of the transformer. When there is a fault inside the transformer, the upper contact of the gas relay is connected to the signal circuit, and the lower contact is connected to the trip circuit of the switch.

12. Housing & Foundation:
Steel or cast iron housing to protect the transformer's internal structure from external physical damage. Provide mechanical support to ensure that the transformer is installed securely.

Key words:
Aceite-transformador de poder lmmersado
Recommended
Transformer maintenance content







